Urban farming is transforming city landscapes, offering sustainable ways to grow food in densely populated areas. One of the most innovative and efficient methods adopted by urban farmers is hydroponics, a soil-free farming technique that conserves space, water, and resources. This article explores how using PVC pipes to create hydroponic systems can revolutionize urban agriculture by providing a simple, scalable solution for growing food in limited spaces.
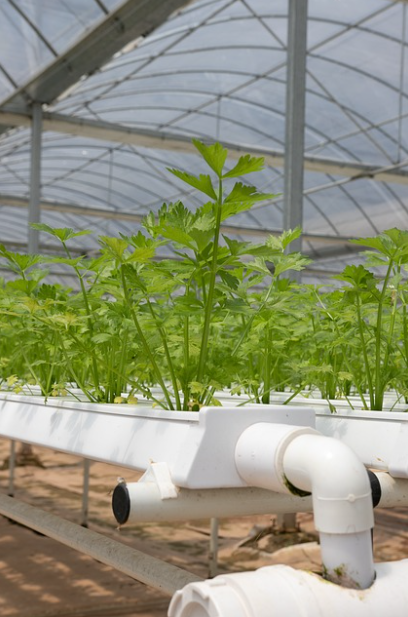

Introduction to Urban Farming with Hydroponics
Urban farming involves growing food in and around cities to reduce the distance food travels and to provide city dwellers with fresh produce. Hydroponics fits perfectly into the urban farming model due to its ability to thrive in small and unconventional spaces. Without the need for soil, hydroponic systems can be set up on rooftops, balconies, or even inside apartments, utilizing every inch of urban space efficiently.
Why Hydroponics is Ideal for Urban Farming
Space Efficiency: Hydroponic systems maximize vertical space through setups like vertical towers or wall-mounted growing systems, making them ideal for cramped city environments. This method allows urban farmers to produce more food per square foot than traditional farming methods.
Water and Resource Conservation: Hydroponics is lauded for its minimal use of water. In these systems, water is recirculated, leading to up to 90% more water efficiency than soil-based gardens. This aspect is particularly crucial in urban areas where water conservation is a priority.
Building a PVC Hydroponic System for Urban Farmers
Building a hydroponic system from PVC pipes is a cost-effective way for urban dwellers to start farming. Here’s how you can build your own:
- Design Your System: Decide whether you want a horizontal or vertical system. Vertical systems are great for balconies or small patios, while horizontal systems might be better suited for rooftops or larger spaces.
- Gather Materials: You’ll need PVC pipes, connectors, a water pump, reservoir, and net pots for holding plants. Tools for cutting and sealing the PVC will also be necessary.
- Assemble the Structure: Cut the PVC pipes to your desired length. For a simple NFT (Nutrient Film Technique) system, drill holes along the top of a horizontal pipe to place your plants. Connect the pipes to your reservoir with a pump to circulate the nutrient solution.
- Install Plants: Insert plants into net pots filled with a suitable inert growing medium like perlite or vermiculite. Position the pots in the prepared holes in the PVC pipe.
Here is a picture of a simple Hydroponics system I am building in my basement. It isn’t pretty, but it doesn’t have to be!
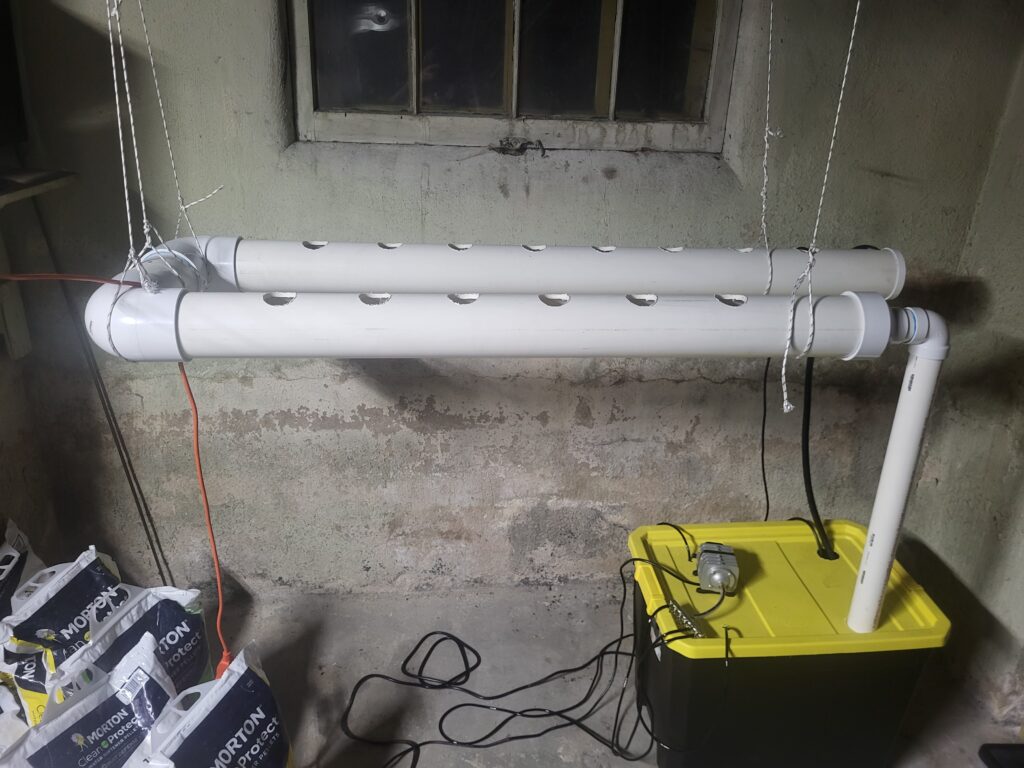

Maintaining Your Urban Hydroponic Garden
Regular maintenance is key to the success of your hydroponic garden. Monitor the nutrient solution’s pH and electrical conductivity daily to ensure optimal plant health. Clean the system regularly to prevent algae growth and inspect the pump and reservoir to avoid clogs. For my first system, I used the following nutrients and they worked great for me.
Benefits of Integrating Hydroponics into Urban Farming
Year-Round Production: Unlike traditional gardening, hydroponics isn’t limited by seasons. This means urban farmers can grow fresh produce all year round, ensuring a constant supply of food. This is the biggest appeal for me being in an area with a harsh winter!
Enhanced Food Security: By producing food locally, urban hydroponics decreases reliance on rural agriculture and long supply chains, enhancing food security in urban areas.
Conclusion: The Future of Urban Farming
Hydroponics represents the future of urban farming, offering a viable solution for growing food in the heart of cities. As urban populations continue to grow, embracing innovative farming techniques like hydroponics will be crucial for building sustainable, resilient food systems.


